About the Author
This article is written by Emily Li, Lead Display Quality Engineer at RisingStar, who brings over 8 years of experience in display manufacturing, defect analysis, and quality control. Emily has led mura detection and calibration projects using both human inspection and automated imaging systems for industrial-grade LCD panels.
Introduction
“Mura,” a Japanese word meaning “unevenness” or “blemish,” refers to non-uniformity in brightness, color, or texture across an LCD display panel—commonly manifesting as patches, streaks, clouding, or spots. These defects significantly degrade display quality and user experience. Understanding, detecting, and mitigating mura is therefore vital for high-reliability display applications such as outdoor digital signage and industrial high-brightness monitors.
(Page original content adapted.)
What Causes Mura?
Mura defects generally result from imperfections in manufacturing or material stress, including:
-
Variations in liquid crystal alignment or layer thickness
-
Non-uniform backlighting or diffuser issues
-
Contaminants or particles within the panel
-
Thermal or mechanical stress during assembly
Real-World Testing Experience (Experience)
At RisingStar, our Quality Engineering team performs multi-stage mura testing on LCD panels sourced from OEMs like LG, BOE, and AUO. Tests include:
-
Visual inspection by trained engineers
-
Gray-level luminance analysis
-
Image subtraction techniques
-
Objective optical measurements using colorimeters and spectroradiometers
These processes are applied both post-panel arrival and post-assembly (including 72-hour aging tests) to ensure only A-grade panels are shipped.
(Page original content summarized.)
Authoritative Insights (Expertise & Authoritativeness)
-
According to Radiant Vision Systems, imaging colorimeters paired with software can objectively identify mura with spatial precision—tools like Just Noticeable Difference (JND) mapping offer rigorous defect quantification.
-
Studies using machine-learning—including CNNs and GANs—demonstrate automated mura detection and classification with over 90% accuracy.
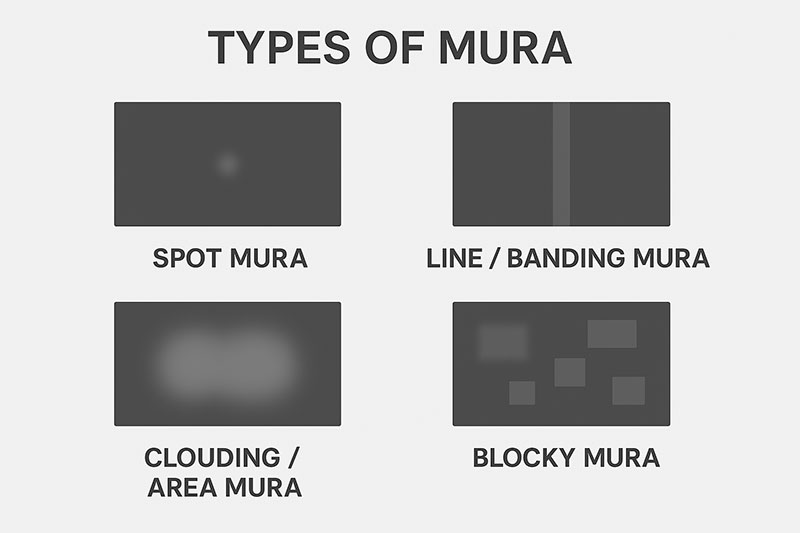
Types of Mura
Common classifications include:
-
Spot Mura: Small bright or dark irregularities
-
Line/ Banding Mura: Horizontal or vertical streaks
-
Clouding / Area Mura: Diffuse patches of uneven brightness
These defects can result from a range of causes such as impurities, uneven substrate bonding, or assembly stress.
Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
-
Manufacturing Optimization: Improve uniformity in backlighting, liquid crystal alignment, and material purity.
-
Automated Quality Control: Incorporate imaging systems and JND-based analysis to detect subtle defects early.
-
Machine-Vision Algorithms: Deploy CNN or GAN models capable of classifying mura types with high accuracy in real-time.
-
Calibration and Uniformity Enhancement: Apply display calibration techniques and optical films to minimize visible inconsistencies.
Update & Trustworthiness
Last updated on August 11, 2025 to include the latest research and testing methodologies. For technical inquiries or custom mura testing solutions, please contact quality@risinglcd.com or leave a comment below.
Disclaimer: All testing and data reflect in-factory conditions; actual results may vary depending on environmental factors, panel suppliers, and display usage scenarios.
Conclusion
Mura significantly impacts display uniformity and user experience. By blending rigorous testing methods, expert analysis, and emerging automated detection technologies, manufacturers like RisingStar ensure only high-quality, A-grade LCD panels reach customers. Optimized mura control elevates display performance in demanding applications such as sunlight readable industrial screens and outdoor signage.
In the world of display technology, one of the most common and frustrating issues that can arise is the presence of mura. Mura refers to the unevenness or inconsistency in brightness, color, or texture across a display panel. It is a phenomenon that can greatly impact the visual quality and user experience of a display, and thus, it is crucial to understand, test, and find solutions for the mura effect problem.
For the LCD display or LCD panel manufacturer, sell the displays to the customers with mura problem will be a totally disaster, that is why we need know and fixed this problem before we sending it.
What is Mura Effect?
Mura, a Japanese term meaning "unevenness" or "uneven texture," is a visual defect that manifests as irregularities in LCD display's uniformity. It can appear as dark or light patches, cloudiness, streaks, or spots on the screen. Mura is primarily caused by variations in the manufacturing process, such as differences in the thickness or density of liquid crystal layers, inconsistencies in backlighting, or imperfections in the display's components.
Mura Test:
To identify and quantify the presence of mura in a display, manufacturers and quality control teams employ a variety of testing methods collectively known as mura tests. These tests aim to assess the uniformity and consistency of a display's visual output. Here are some commonly used mura testing techniques:
1. Visual Inspection: The simplest and most intuitive method is a visual inspection by trained experts who carefully examine the display for any visible irregularities. This subjective approach can be effective for detecting obvious mura problems but may not be suitable for identifying subtle defects.
2. Gray-Level Analysis: This method involves displaying a series of gray-level patterns on the screen and analyzing the measured luminance values. Comparing the luminance levels across different regions of the display helps identify any mura-related variations.
3. Image Subtraction: By capturing images of a display with a uniform background and subtracting them from each other, any differences between the images can be highlighted. Mura defects will appear as deviations from the expected uniformity.
4. Optical Measurement: Utilizing specialized equipment like spectroradiometers or colorimeters, optical measurements can be taken across the display to quantify mura. These measurements provide objective data on color and luminance variations.
All these test finished by our test engineer when the LCD open-cells from LG/BOE/AUO arrived our factory; doing again before the LCD panels will leave our factory, also the LCD displays/panels are already finished the 72 hours aging test.

Types of Mura Problems:
Mura problems can manifest in various forms, each with its own characteristics and impact on the display's performance. Some common types of mura problems include:
1. Clouding: Clouding refers to the appearance of uneven backlighting, resulting in cloudy patches or areas of different brightness on the screen. It is often caused by backlight inconsistencies or improper light diffusion.

2. Banding: Banding appears as horizontal or vertical lines of varying brightness or color intensity across the display. It is typically caused by non-uniform pixel response times or variations in the driving voltage.

3. Spotting: Spotting refers to the presence of dark or bright spots on the screen, which can be caused by impurities in the liquid crystal material or defects in the manufacturing process.

4. Mura Noise: Mura noise is a term used to describe random fluctuations in brightness or color across the display. It can result from variations in the liquid crystal molecules' alignment or non-uniform electric fields.
Solutions for mura effect problem:
Addressing mura problems requires a combination of manufacturing improvements, quality control measures, and display calibration techniques. Here are some common solutions employed in the industry:
1. Manufacturing Process Optimization: Manufacturers can refine their production processes to minimize variations in component quality, thickness, and density. This involves enhancing the precision of liquid crystal alignment, improving backlight uniformity, and reducing impurities.
2. Quality Control Testing: Implementing rigorous mura testing at various stages of production helps identify and rectify any defects early on. This includes visual inspection, gray-level analysis, and optical measurements to ensure consistent quality.
3. Compensation Algorithms: Display manufacturers can develop compensation algorithms that dynamically adjust the display output to mitigate mura effect. These algorithms analyze the mura patterns and apply corrective measures to enhance uniformity.
4. Display Calibration: Users can employ display calibration techniques to optimize the visual quality of their displays. This involves adjusting parameters like brightness, contrast, and gamma settings to compensate for any mura-related inconsistencies.
5. Display Uniformity Enhancement Films: Specialized films can be applied to the display surface to enhance the uniformity of light transmission. These films help diffuse light and reduce the visibility of mura-related irregularities.
All RisingStar screens purchased from LG/BOE/AUO directly, use A+ grade LCD panels and our team will do double test before the products are packaging.

 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français Español
Español Italiano
Italiano 한국어
한국어 日本语
日本语 Português
Português Suomi
Suomi Dansk
Dansk Polski
Polski